Open Source Project
Beam Inspector

C. Franke, K. Fritsch, O. Pronin , N. Chunosov
We regularly need to measure the laser beam profile of femtosecond lasers in the lab at each workstation. This beam characterization is necessary to ensure that the mode-matching of our multipass cells fits accurately to our customers’ lasers. Additionally, we frequently include beam profilers with our modules as a useful tool to facilitate the remote installation of our pulse shortening (MIKSs) modules. Unfortunately, ordering a new commercial-grade laser beam profiler in every case is not affordable, and the full feature set is mostly not required for our application.
We decided to sponsor the development of minimalistic, easy-to-use laser beam profiler software for widely available industrial cameras and open source the whole project under the GNU GPL v3.0 license for you to use!
Nikolay Chunosov, known from his reZonator project [1], wrote the software.
The n2-Photonics team tested the software in the lab and financially supported the project.
Currently, only IDS cameras supporting the IDS peak software (GenICam) are supported. The following cameras are tested:
IDS U3-3680XCP-NIR Rev.1.2 (recommended max. beam diameter: 2.8 mm @ 1/e²) [2]
IDS U3-3180CP Rev. 2.2 (recommended max. beam diameter: 3.9 mm @ 1/e²) [3]
Commercial-grade beam profilers usually remove the cover glass on top of the sensor since it can introduce measurement artifacts (secondary reflections or interference fringes for coherent radiation [4]). We usually do not remove the protective glass from IDS cameras since the coherence length of our femtosecond pulses (<300 fs) is short enough to avoid artifacts. However, your experience may vary.
Beam Inspector can be downloaded here [5]
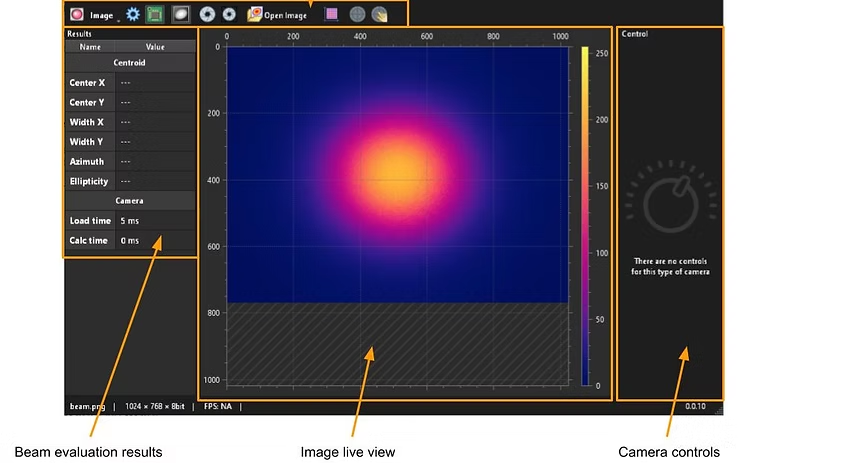
Basic control of the camera exposure parameters (exposure time, analog & digital gain)
Laser beam width, position, and ellipticity measurements according to ISOs 11146-1, 11146-2 and 11146-3.
Background subtraction
Area of interest selection
Laser beam parameter tracking for stability measurements
Beam position reference overlay
Analysis of static images
Variable color maps (perceptually uniform ones are recommended [6])
Feedback is highly appreciated either on the github or under info@n2-photonics.de!
USB 2.0 instead of USB 3.0
Noise visible in upper quarter of the image
Bottom ¾ of the image are completely blank
Camera LED solid orange color (no blinking)
USB 2.0 instead of USB 3.0
Noise visible in upper quarter of the image
Bottom ¾ of the image are completely blank
Camera LED solid orange color (no blinking)
USB 2.0 instead of USB 3.0
Noise visible in upper quarter of the image
Bottom ¾ of the image are completely blank
Camera LED solid orange color (no blinking)
Feedback is highly appreciated either on the github or under info@n2-photonics.de!
[1] http://www.rezonator.orion-project.org/
[2] https://de.ids-imaging.com/store/u3-3680xcp-nir-rev-1-2.html
[3] https://de.ids-imaging.com/store/u3-3180cp-rev-2-2.html
[4] https://www.eureca.de/files/glasscoverremoval_
2019-09-24.pdf
[5] https://github.com/orion-project/beam-inspector/releases
[6] Crameri, F., Shephard, G.E. & Heron, P.J. The misuse of colour in science communication. Nat Commun 11, 5444 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-19160-7